When installing a wood stove in your home, understanding wood stove heat shield requirements is critical for both safety and building code compliance. A properly installed heat shield not only protects your home from the intense heat produced by a wood stove, but it also allows for safer installation closer to walls and floors. This essential component can make or break a safe wood stove setup, yet it’s often misunderstood or overlooked by DIYers and even some contractors.
In this article, we’ll break down the importance of heat shields, explore different types of wood stove heat protection, explain clearance reduction techniques, and give you practical guidance to ensure your installation meets NFPA 211 standards and local building codes.
Why Understanding Wood Stove Heat Shield Requirements Matters

Wood stoves generate intense heat, especially when used for extended periods during winter. If installed too close to a combustible surface such as drywall, paneling, or wood framing, this heat can cause materials to smolder, degrade, or even ignite. Many homeowners are unaware of how specific wood stove heat shield requirements can impact where and how they install their unit.
That’s where heat shields come in. A heat shield acts as a thermal barrier, allowing you to reduce the distance between the stove and nearby walls or floors. This doesn’t just protect your home, it gives you more flexibility in where you place the stove, especially in smaller rooms or cabins.
According to fire safety experts and most building codes, a stove installed without proper shielding must maintain a 36-inch clearance from combustible walls. With a correctly constructed and ventilated heat shield, this clearance can often be safely reduced to 12 inches or less, depending on the stove model and shield type.
Types of Heat Shields for Wood Stoves
There are several types of heat shields, each serving a slightly different purpose. The right one for you depends on your installation environment and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
1. Wall-Mounted Heat Shields
These are typically constructed from:
- Sheet metal (galvanized steel or aluminum)
- Ceramic fiber board
- Tile or masonry mounted on fire-rated board
The key feature is the air gap behind the shield, usually 1 inch created using non-combustible spacers. This air gap promotes convection cooling and is critical to the shield’s effectiveness.
2. Stove-Mounted Heat Shields
Some stoves come with integrated rear and bottom heat shields, which help reduce required clearances right out of the box. Aftermarket models are also available and must be installed according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
3. Floor Heat Shields (Hearth Pads)
If you’re installing a stove on a combustible surface, such as hardwood or carpet, a floor heat shield or hearth pad is mandatory. These shields are made from materials like tile, stone, or UL-listed hearth boards. And if you’re upgrading or doing repairs, don’t miss our detailed wood stove glass door replacement guide.
Tip: Always check the manufacturer’s manual. Clearance reduction values vary depending on the shield material and configuration.
Heat Shield Clearance Guidelines
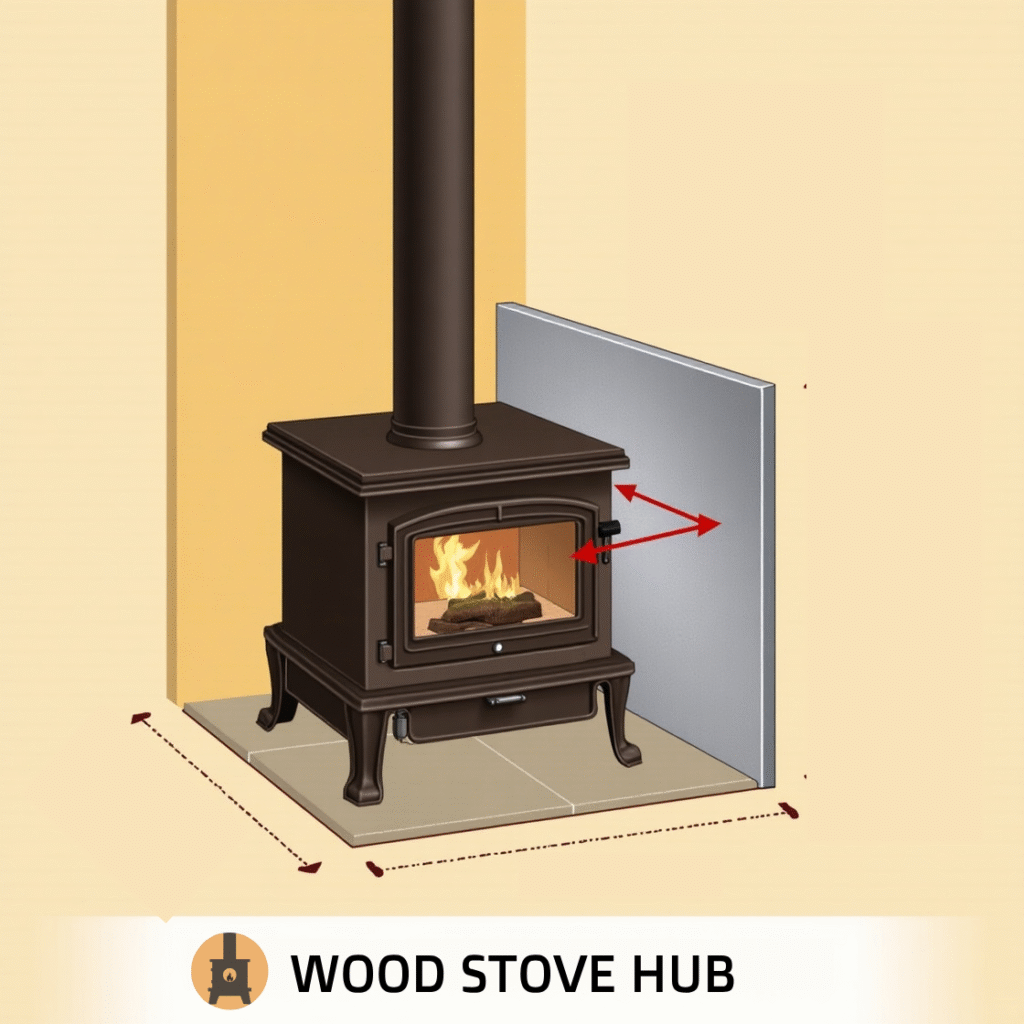
For an installation to be code-compliant and safe, you must follow specific guidelines on clearances and construction techniques.
Wall Clearance with and without Shield
| Setup Type | Required Clearance |
|---|---|
| No heat shield | 36 inches |
| With ventilated heat shield | 12–18 inches |
| With stove-mounted shield | Depends on model |
Additional Code Requirements:
- The shield must extend at least 18 inches above and to the sides of the stove.
- Bottom edge should be 1 inch above the floor to allow air circulation.
- Spacers used to create air gaps should be non-combustible (metal or ceramic).
- The air space must be open at the bottom and top for airflow.
6 Key Wood Stove Heat Shield Requirements:

- Maintain at least 36″ clearance without a heat shield or reduce to 12″–18″ with proper shielding.
Most building codes require a minimum of 36 inches between the stove and any combustible wall. However, with a well-built heat shield in place, that distance can legally and safely be reduced to as little as 12 inches, depending on your local regulations and stove model. - Use 24-gauge sheet metal, tile, or UL-listed board as your shield material.
Choose a durable, fire-resistant material. Galvanized steel, tile over cement board, or UL-listed wall protectors all meet common code standards. Always verify that the material matches the stove manufacturer’s recommendations. - Create a 1-inch ventilated air gap using non-combustible spacers.
The shield must not sit flush against the wall. Use metal or ceramic spacers to maintain a consistent 1-inch gap behind the shield, this airflow is crucial to prevent heat buildup and improve fire safety. - Make sure the shield extends 18 inches past the sides and top of the stove.
This extended coverage helps protect nearby surfaces from radiant heat and is often a specific code requirement. Measure carefully and plan for a generous safety margin. - Keep the top and bottom of the shield open to allow airflow.
An open gap at both the top and bottom edges of the shield promotes natural convection. This airflow pulls cooler air behind the shield and exhausts warmer air upward, preventing overheating of the wall. - Use UL 1618-rated materials when possible, and check NFPA 211 for code compliance.
UL 1618 certification ensures that the product has been tested for wall protection under high temperatures. Always cross-reference your setup with NFPA 211 standards and your local building department’s guidelines to avoid surprises during inspection.
How to Install a Wood Stove Heat Shield
If you’re planning a DIY wood stove installation, here’s a step-by-step approach to creating a compliant wall heat shield:
When building your wall protection, make sure to meet or exceed the recommended wood stove heat shield requirements from both the manufacturer and NFPA.
Materials:
- 24-gauge sheet metal or equivalent non-combustible material
- 1-inch ceramic spacers or metal washers
- Fire-resistant screws
- Metal furring channels (optional)
Steps:
- Mark your layout to cover at least 18 inches beyond each side of the stove.
- Mount the spacers to wall studs to create a 1-inch air gap.
- Attach the sheet metal or heat-resistant board to the spacers.
- Leave a 1-inch gap at the bottom and top to allow air circulation.
Make sure to double-check all measurements against your stove’s installation manual and NFPA 211 or local fire code requirements.
Code Compliance and UL Listing
The most trusted guidelines for wood stove installations come from NFPA 211, which is widely adopted by building departments across North America. It provides standards for:
- Chimney design
- Heat shield construction
- Clearance requirements
- Combustion air and ventilation
Whenever possible, use UL-listed heat shield materials and products. For example, UL 1618-rated wall protectors meet rigorous fire resistance standards and are accepted by code enforcement officers.
Before installing, always consult your local building department or fire marshal. Many jurisdictions require a permit and inspection for solid-fuel appliance installations.
Best Practices for Heat Shield Maintenance
- Inspect annually for rust, cracking, or deformation.
- Clean behind the heat shield to prevent dust buildup, which can become flammable. For related maintenance, check out our guide on how to clean your wood stove chimney yourself.
- Re-check all fasteners and spacers to ensure the air gap is maintained.
- Watch for warping or discoloration, which may indicate overheating.
Proper maintenance ensures your shield continues to offer the fire protection it was designed for.
Summary: Stay Safe and Legal
Understanding wood stove heat shield requirements is more than just a technicality, it’s a core part of keeping your home and family safe. Whether you’re installing a freestanding stove in a living room, a corner fireplace unit in a cabin, or an outdoor shed heater, following these guidelines will help you stay code-compliant and protect your property.
Don’t forget:
- Maintain proper clearances
- Use the correct materials
- Install shields with ventilation gaps
- Check local codes and permit requirements
With careful planning and proper installation, your wood stove can be a safe, efficient, and long-lasting heat source for years to come. By following these wood stove heat shield requirements, you can rest assured that your installation is both code-compliant and safe for your family.







Where can you buy quality heat shields in the US?
I am seeing perfect vitreous ones but they are in the UK.
Thank you
You can find good, U.S made heat shields from American Panel, DuraVent, or Drolet. all well-known and trusted brands here. They make solid, UL-listed wall and hearth shields that fit most woodstove setups. The glossy vitreous-enamel style you’re seeing in the UK isn’t common in the U.S, so you’d likely have to import those if that’s the look you want.
Could you please send specifications for installing wood heater in a home in NOVA SCOTIA CANADA ( measurements shield requirements etc) through the wall stainless flue. thanks. I found your browser page very informative however i am one that needs to see the info in front of me —thanks LLOYD
Hi Lloyd, thanks for the kind words, happy to help 👍
For Nova Scotia (Canada), wood stove installs follow CSA B365 plus the stove manufacturer’s manual.
Quick specs you can reference:
Clearance to combustibles:
• 36″ (915 mm) with no heat shield
• Can be reduced to 12-18″ with a proper ventilated heat shield (1″ air gap, open top & bottom)
Heat shield:
• Non-combustible (24-ga steel, cement board + tile, etc.)
• Extend 18″ (450 mm) past stove sides and top
Hearth protection:
• 18″ in front of loading door, 8″ on sides/rear (or per stove manual)
Through-the-wall chimney:
• ULC-listed Class A stainless
• 2″ clearance to combustibles
• Use a listed wall thimble and firestop
Always follow the stove manual first and check with your local building/fire office for permits and inspection.
Hope that helps!